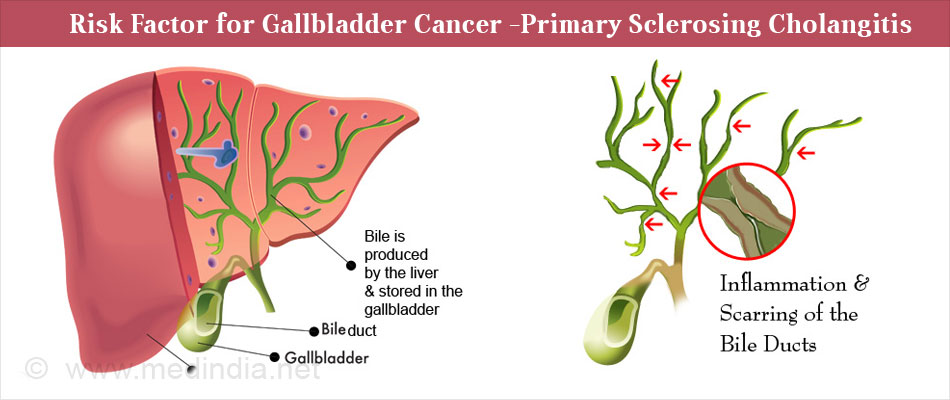
Gallbladder cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the <
Your risk of getting gallbladder cancer increases as you get older. Most people who develop it are aged between 85 and 89. Remember, the risk is still small because this is rare cancer.
Gallbladder cancer is more common in women than men. 71 out of 100 people diagnosed with gallbladder cancer (71%) are women
Signs and symptoms of gallbladder cancer include jaundice, fever, and pain.
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by gallbladder cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
Tests that examine the gallbladder and nearby organs are used to detect (find), diagnose, and stage gallbladder cancer.
Procedures that make pictures of the gallbladder and the area around it help diagnose gallbladder cancer and show how far the cancer has spread. The process used to find out if cancer cells have spread within and around the gallbladder is called staging.
In order to plan treatment, it is important to know if the gallbladder cancer can be removed by surgery. Tests and procedures to detect, diagnose, and stage gallbladder cancer are usually done at the same time. The following tests and procedures may be used:
Treatment Option Overview
KEY POINTS